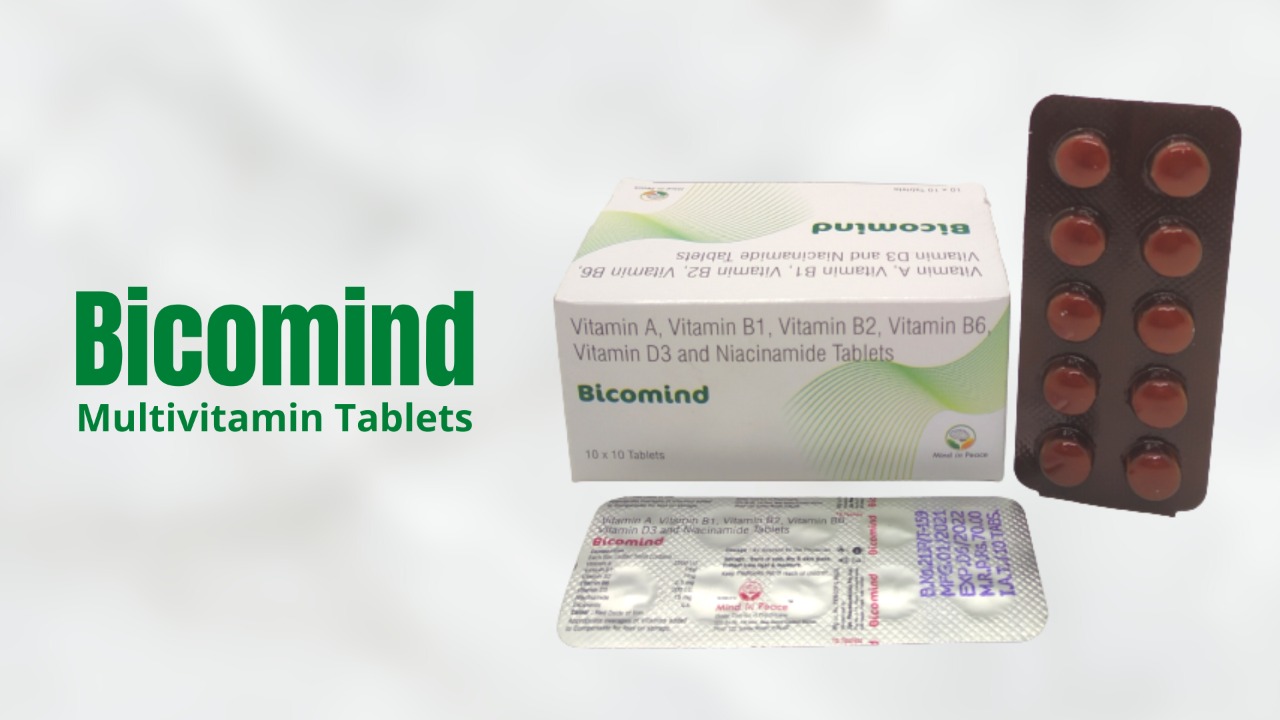
Vitamin B2
Water-soluble vitamin B2, sometimes called riboflavin, is naturally present in several foods. Like vitamin B1, the body cannot produce riboflavin also. Small amounts of it are stored in the liver after being absorbed into the small intestine during digestion. The body releases extra riboflavin in the urine after it has been passed through the bloodstream. This is the reason why foods rich in Vitamin Bs are recommended to be eaten daily.
The B vitamins group helps the body produce sugar in the diet (carbohydrates). These vitamins, also called B-complex vitamins, support both protein and fat metabolism. To maintain healthy skin, hair, and eyes, B-Complex vitamins are needed. They also support the maintenance of the nervous system.
Additionally, the body needs riboflavin to convert vitamin B6 and folate into forms that may be utilised. The growth process and the creation of red blood cells both depend on it. Most healthy individuals who consume a diet that is well-balanced obtain adequate riboflavin. However, due to inadequate food, older persons and drinkers may be at risk for riboflavin deficiency. The following are signs of riboflavin deficiency:
• Fatigue
• Sluggish growth
• Digestion issues
• Around the mouth’s corners, there are cracks and sores.
• Magenta-colored tongue enlargement
• Fatigued Eyes
• Throat swelling and discomfort
• Light Sensitivity
Assists in the breakdown of proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates is vitamin B2. It is crucial for sustaining physical strength.
Adenosine triphosphate is produced from carbs with the aid of riboflavin (ATP). Food is converted into ATP by the human body, and ATP generates all the energy required by the body. For muscles to stay strong, compound ATP is necessary.
Vitamin B is necessary in addition to vitamin A for:
– Maintaining the digestive system’s mucous membranes.
– Keeping the liver healthy.
– Transforming tryptophan into the amino acid niacin.
– Iron and activate iron, folic acid, and the vitamins B1, B3, and B6 maintain the health of the Eyes, emotions, muscles, and skin.
– The adrenal glands produce hormones.
– Avoiding the emergence of cataract.
– Growth of children, particularly in regions where vitamin deficits are prevalent.









Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!